There are several reasons why you may experience bleeding. Fortunately, many of the reasons that cause bleeding gums are reversible with behavioural changes and healthy practices. However, if ignored, serious health issues can result.
We are going to look at the four main reasons for bleeding gums so you can identify them and correct if necessary, including plaque and tartar build-up, gum disease, improper brushing techniques, or poor nutrition.
Plaque and Tartar
Plaque and tartar are the main causes of bleeding gums. Plaque is a sticky film that forms over teeth. Tartar is hardened plaque that builds up over time, blocking the tiny spaces between your teeth where bacteria grow. Tartar can only be removed by your dentist or oral hygienist.
Both plaque and tartar cause inflammation of the gums, or gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis may progress to periodontitis, an inflammatory disorder that causes damage to the tissues supporting your teeth (periodontal tissues) and bone loss around them.
Periodontitis (Gum Disease)
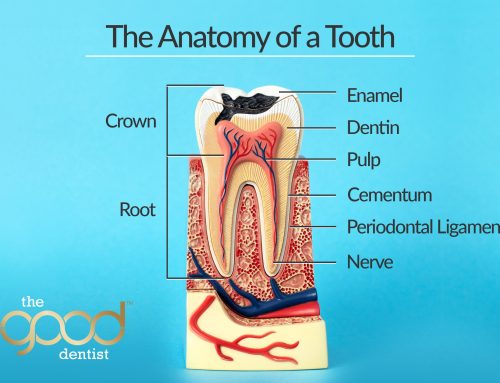
Gum disease or periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium, which includes the gums, cementum, and alveolar bone surrounding your teeth. Gum disease is usually caused by plaque which can harden into tartar (also called calculus) if not removed.
This condition can cause the pocket around your tooth to deepen and enlarge, allowing bacteria to enter into the tissue and cause inflammation. The inflammation can lead to red, swollen, and sore gums around your teeth plus other unpleasant symptoms such as bad breath and redness of the tongue or the taste of infection. Periodontitis can lead to loosened teeth or tooth loss if not treated properly by your dentist or hygienist.
If you have these symptoms and suspect that you might have periodontitis, talk to a dentist who can diagnose it with a thorough examination of both your mouth and medical history. Bleeding gum treatment may involve scaling (removing tartar) and root planing (shaping tooth roots.)
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the early stages of periodontitis which also causes inflammation and breakdown of tissue and bone supporting the teeth. Although reversible with regular brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups, a number of factors can increase your risk for developing gingivitis such as smoking and diabetes (high blood sugar.)
Gingivitis does not necessarily progress to periodontitis as long as you seek treatment and maintain consistent oral hygiene practices.
Improper Tooth Brushing Techniques
Good brushing techniques are a major factor in preventing bleeding gums, gum disease, and tooth decay. There are several top techniques for good oral health that should be practised every day, but the key is to be gentle. Aggressive brushing with hard-bristled toothbrushes can cause more harm than good. Try the following techniques.
- Floss daily to remove food particles trapped between the teeth or on the gums
- Brush teeth twice daily for two minutes using a medium toothbrush or an electric toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste
- Brush your entire mouth using circular motions including your tongue
Poor Nutrition
In order to maintain healthy gums, it is important that you eat a balanced diet. You should consume foods that promote oral health and avoid those that cause gum inflammation or increase the risk of developing gum disease.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables because they are rich in antioxidants, which help prevent plaque build-up on your teeth and gums
- Avoid sugary drinks since they promote tooth decay and can damage soft tissue inside your mouth
- Try not to snack if possible as snacking throughout the day leaves your mouth in an acidic environment which promotes bacteria
If you notice that you have inflamed or sore gums, don’t panic – but it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Bleeding gums can be a sign of more serious health problems, including gum disease and periodontitis, which can ultimately lead to tooth decay and tooth loss.